What Is Testosterone Deficiency?
Testosterone deficiency is when your body is not producing enough testosterone.
There can be several causes for a testosterone deficiency, but the most common reason for low testosterone is the steady decline in testosterone that occurs as men and women age. Doctors refer to this condition as an “age-related testosterone deficiency.”
Testosterone deficiency can be a problem for men or women. A testosterone deficiency can be a problem because testosterone is a major hormone that regulates or influences many of the bodily processes that keep you strong and vital.
Doctors who treat low testosterone recognize two types of testosterone deficiencies: primary and secondary testosterone deficiency.
Primary Testosterone Deficiency
When you have a primary testosterone deficiency, that means that you don’t have enough testosterone due to a problem in the organs that make testosterone. In men, that is the testes, and in women, that is the ovaries or the adrenal glands. In a primary testosterone deficiency, the source of testosterone production in your body is still receiving the message from the brain to produce testosterone, but the organs are unable to produce the hormone.
Secondary Testosterone Deficiency
In a secondary testosterone deficiency, there is a problem in the areas of the brain that signal the sex organs to make or release testosterone. This type of testosterone deficiency means that you have a problem in the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland — the parts of the brain that tell the testicles to produce testosterone. The hypothalamus produces gonadotropin-releasing hormone, which signals the pituitary gland to make follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Luteinizing hormone then signals the testes to produce testosterone.
Causes of Testosterone Deficiency
Either type of testosterone deficiency can be caused by an inherited (congenital) trait or something that happens later in life (acquired), such as an injury or an infection. Often primary and secondary testosterone deficiency occur together.
Several factors can contribute to an acquired testosterone deficiency. Not getting enough exercise, doing the wrong kinds of exercise, a poor diet, and metabolic conditions such as diabetes can lead to low testosterone. However, the most likely cause of testosterone deficiency is the normal drop in testosterone levels that occur as you age.
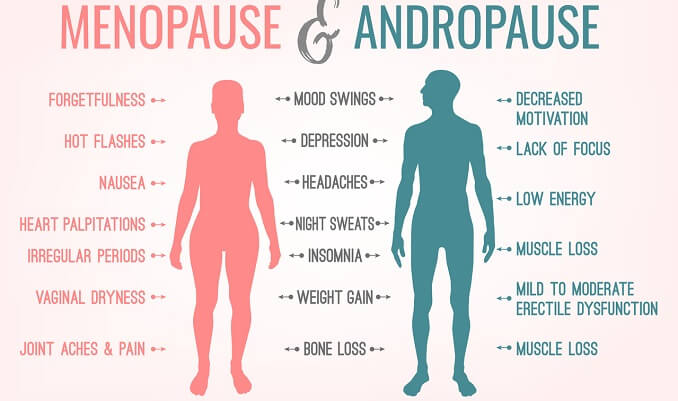
While there can be many reasons for testosterone deficiency, the condition primarily affects older men. This is because once a man is over 30, the level of testosterone in his blood starts to drop significantly. This type of age-related testosterone deficiency in men is similar to menopause in women. It is, therefore, sometimes referred to as “andropause.” However, unlike menopause, which happens at a specific time in a woman’s life, andropause in men develops more slowly over time. Once a man is over 40, his testosterone level will drop by as much as 2% per year. By age 70, the average man’s testosterone production is about half of what it was in his 20s.
Testosterone levels are measured in nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL). Typically, the normal range is 300 to 1,000 ng/dL. Anything below 300 ng/dL is considered low testosterone.
What Are the Symptoms of Testosterone Deficiency?
Many of the signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency overlap between men and women. However, there are some symptoms of testosterone deficiency that are only experienced by women, and some that are only felt by men.
Generally, testosterone deficiency impacts three major areas of your life: your physical well-being, your emotional well-being, and your mental acuity. Broadly, testosterone deficiency signs and symptoms are a decreased sex drive, fatigue, weight gain, loss of muscle and bone mass, and changes in mood.
There are several signs and symptoms that can be associated with a testosterone deficiency in in men and women:
- Reduced libido
- Difficulty obtaining or maintaining an erection (men)
- Vaginal dryness, or painful intercourse (women)
- Low sperm counts/fertility issues (men)
- Worsening of menopausal symptoms (women)
- Loss of focus and concentration
- Mood swings and anxiety
- Inability to build muscle, even while exercising
- Increase in body fat
- Memory loss and other cognitive difficulties
- Loss of lean body (muscle) mass
- Loss of bone density
Testing for Testosterone Deficiency
The only way to determine if you have a testosterone deficiency is to have your testosterone levels tested. This is usually done with a simple blood test. In addition to having your testosterone level tested, your doctors will take a complete medical history and do a thorough medical exam before offering a diagnosis of low testosterone.
Any doctor can perform a blood test for low testosterone. However, if you suspect that you have a testosterone deficiency, it is best to be tested by a doctor who specializes in age-related hormone imbalances in men and women.
Treatment for Testosterone Deficiency
Regardless of how many of the signs and symptoms of low testosterone you are exhibiting, testosterone deficiencies in men and women are treated the same way – with testosterone replacement therapy.
Testosterone therapy is only available with a doctor’s prescription. Your doctor will prescribe testosterone replacement after your testosterone levels have been tested. If your levels are low enough to be diagnosed with a testosterone deficiency, you will be prescribed testosterone replacement therapy.
Our doctors have found that testosterone injections are the safest and most effective form of testosterone therapy. You cannot buy testosterone injections online or without a doctor’s prescription.
If you are experiencing the signs and symptoms of testosterone deficiency, you can obtain a prescription for testosterone injections by following these five simple steps:
- Step 1 – Fill out an online medical history form – This first step is indeed the only step in the process of getting testosterone injections that can be done online.
- Step 2 – See a doctor –If your online medical history form indicates that you are a good candidate for testosterone therapy, the next step is to see your doctor. He or she will discuss your medical history in further detail, ask you more about your symptoms, and take a complete physical exam.
- Step 3 – Laboratory hormone testing – Once you have completed your physical exam, you will be referred to a laboratory to have the testosterone levels in your blood tested.
- Step 4 – You will obtain a prescription for a program of testosterone injections – If the results of your laboratory tests show that your testosterone levels are low, your doctor will prescribe dosage and type of testosterone injections to suit your needs and lifestyle.
- Step 5 – Your testosterone will be delivered to you – Your prescription for HGH therapy will be forwarded to one of the pharmacies we work with that specializes in filling prescriptions for testosterone injections. The pharmacy will then deliver your testosterone therapy supplies to you.
FAQs
How do I know if I have a testosterone deficiency?
Suppose you are over 40 and experiencing sexual health issues, feeling tired, depressed, and putting on weight even while exercising. In that case, there is a chance that the cause is age-related testosterone deficiency. However, the only way to know for sure is to have the testosterone levels in your blood tested.
Is the treatment for testosterone deficiency safe?
When taken correctly with proper medical supervision, testosterone injections are the safest and most effective way to treat men and women with testosterone deficiency.
Are there any ways to boost testosterone?
The only way to treat a diagnosed testosterone deficiency is with testosterone replacement. However, there are some ways you may be able to naturally maintain a normal testosterone level, such as:
- Exercise, particularly strength training and lifting weights.
- Eat a diet high in protein and low in fat and carbs.
- Minimize stress.
- Increase vitamin D via supplement or spending more time outdoors.
- Take some vitamin and mineral supplements such as Zinc and B-vitamins.
- Get plenty of restful, high-quality sleep.
Can testosterone deficiency lead to erectile dysfunction?
Yes! One of the first symptoms that men with low testosterone notice are a decrease in sex drive and sexual performance. Testosterone is a precursor to the release of nitric oxide during sexual arousal, which starts several reactions that result in an erection. Therefore, a testosterone deficiency can lead to ED.
Can a testosterone deficiency cause depression?
The testosterone receptors in your brain crave testosterone. When you have low testosterone, these receptors are literally starved of testosterone, which can lead to:
- Mood swings
- Irritability
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Depression
A testosterone deficiency’s impact on the brain not only affects cognitive function but emotional states as well.
Does testosterone deficiency cause weight gain?
Yes. Another quite common symptom of testosterone deficiency is weight gain, particularly belly fat. Low testosterone reduces your ability to burn fat and increases insulin resistance, both of which can lead to obesity.
What diseases can result from having a testosterone deficiency?
Besides the signs and symptoms above, testosterone deficiencies can cause other negative effects on your health and well-being and some specific conditions such as:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
- Increased risk of death from a cardiovascular event
- Increased risk of metabolic syndrome: high blood pressure, elevated insulin levels, excess belly fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels
- Strong association with diabetes
- Strong association with atherosclerotic disease of the aorta
- Higher incidence of prostate cancer
- Association with more aggressive variants of cancer
Now that you know a little bit more about testosterone deficiency, how to recognize it, and how to treat it, why not take a minute to contact us and learn more about how hormone replacement therapy can improve your quality of life?